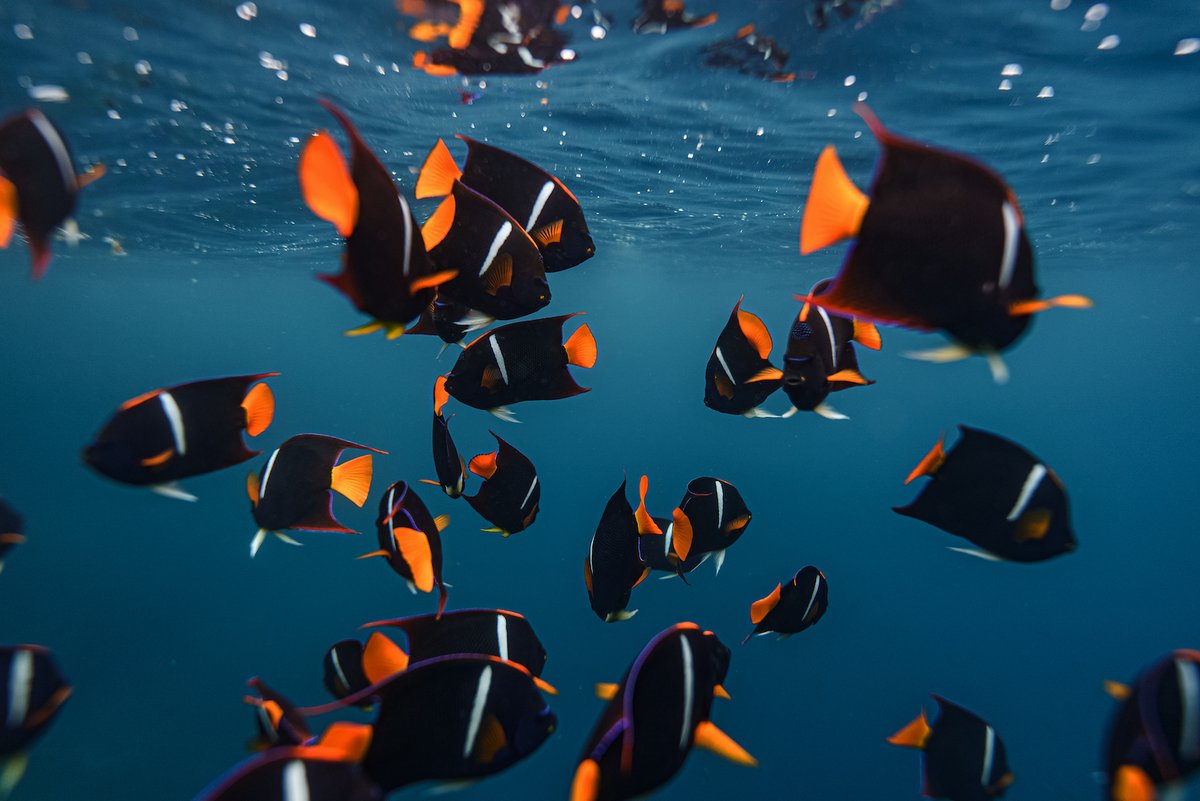
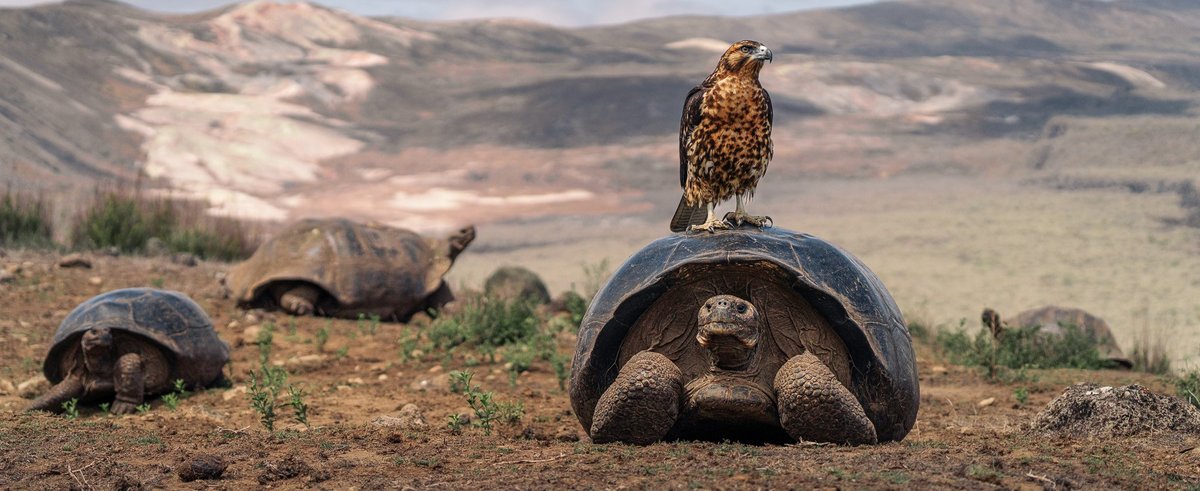
Results

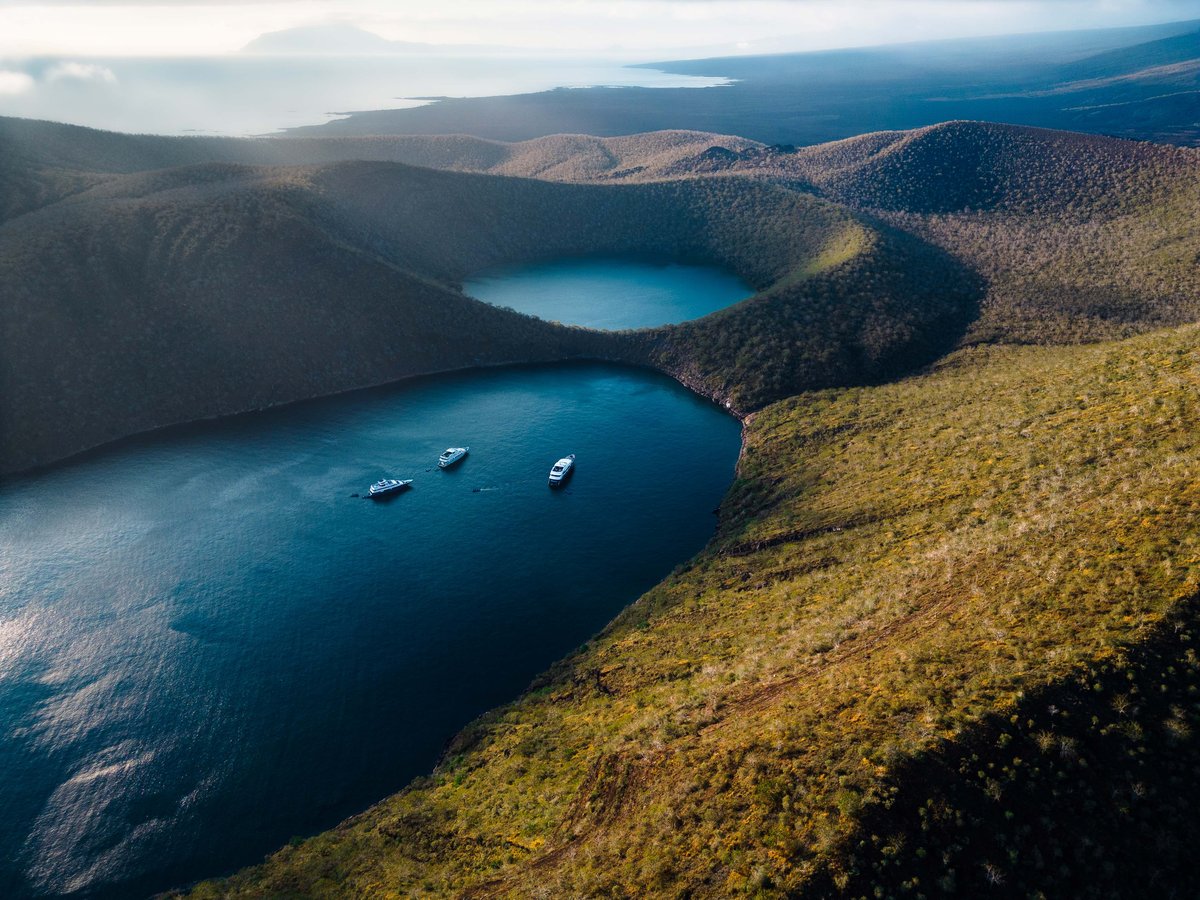
Discover how Galápagos waters fuel Ecuador’s economy and fight climate change. A groundbreaking study by CDF and partners reveals the immense value of marine ecosystems—from carbon-storing mangroves to booming tourism and fishing industries. Learn why protecting these waters is essential for sustainable development and global conservation efforts.

The Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF) is pleased to announce that 16 individuals of the rare plant Scalesia retroflexa were found growing on the steep, rocky coastal slopes of the southeastern point of Santa Cruz Island. Scientists from CDF’s Galapagos Verde 2050 ecological restoration team, in collaboration with rangers from the Galapagos National Park Directorate (GNPD), made this discovery during a recent expedition, renewing hope for the survival of this endemic species.

The Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF) is pleased to announce that 16 individuals of the rare plant Scalesia retroflexa were found growing on the steep, rocky coastal slopes of the southeastern point of Santa Cruz Island. Scientists from CDF’s Galapagos Verde 2050 ecological restoration team, in collaboration with rangers from the Galapagos National Park Directorate (GNPD), made this discovery during a recent expedition, renewing hope for the survival of this endemic species.

The world conservation movement and the Galapagos Islands lost a passionate supporter, pioneering conservationist, mentor and friend with the death of Dr. Craig George MacFarland in April 2025.

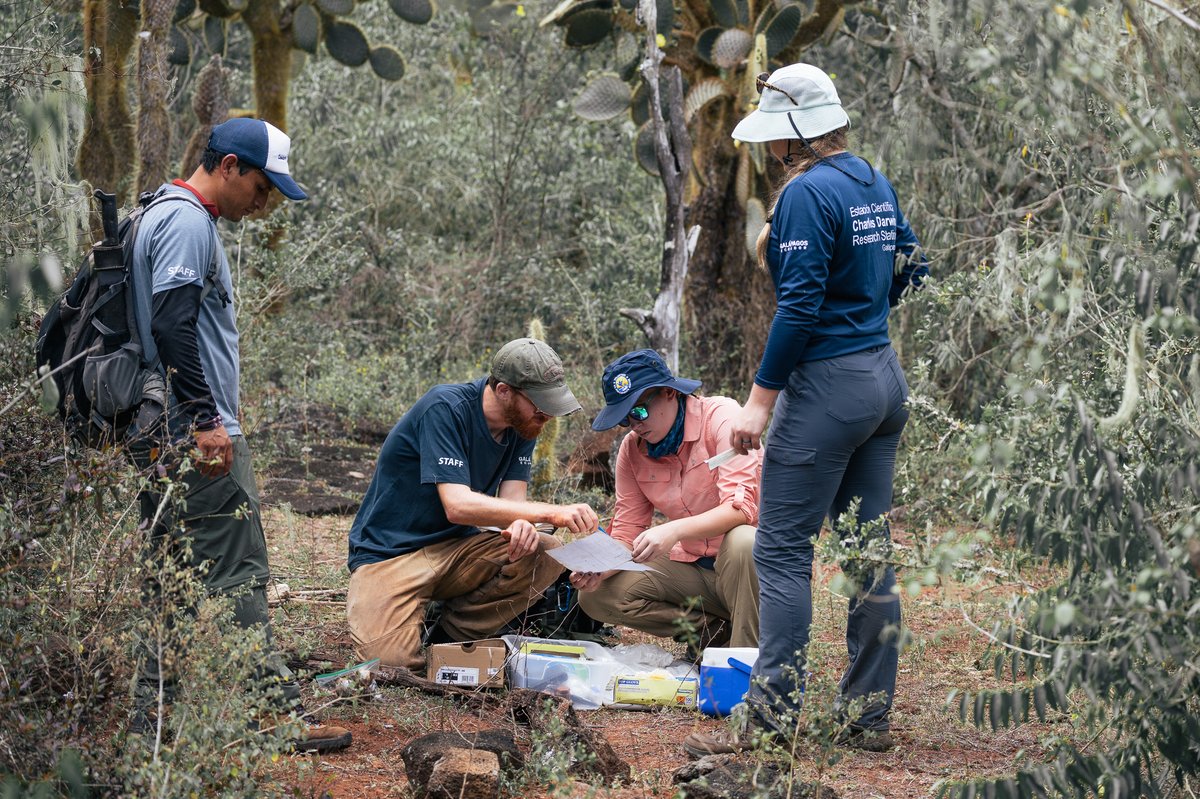
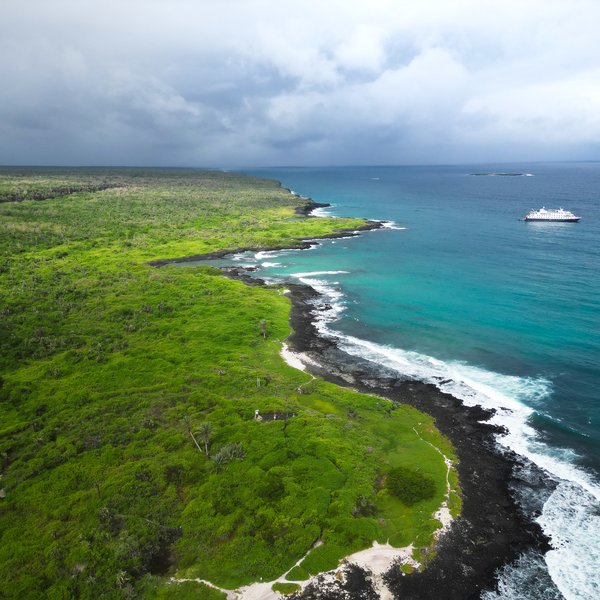
The CDF joins the Island-Ocean Connection Challenge to Implement Community-Based Monitoring and Safeguard Island Ecosystems
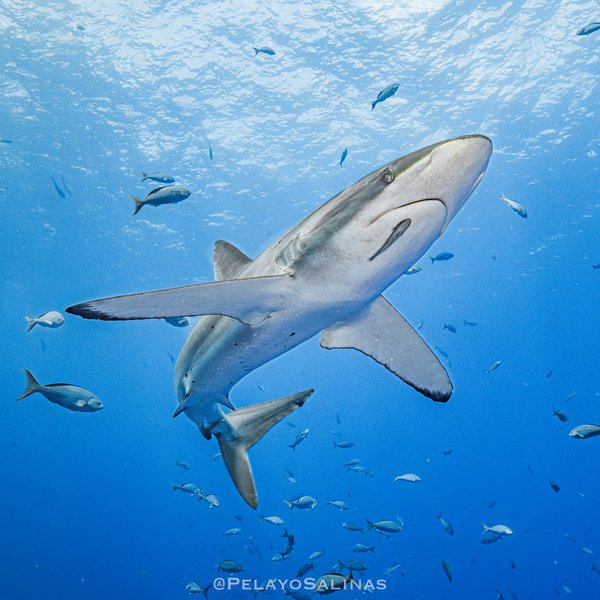

Silky shark's record-breaking migration of more than 27,000 km on the Tropical Eastern Pacific sheds light on urgent conservation need

Silky shark's record-breaking migration of more than 27,000 km on the Tropical Eastern Pacific sheds light on urgent conservation need

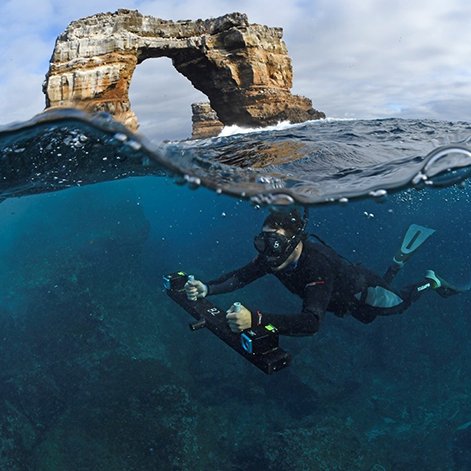
A scientific team led by the Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF) and the California Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with the Galapagos National Park Directorate (GNPD) has confirmed that Rhizopsammia wellingtoni—a solitary coral thought to be lost for a generation— is alive and clinging to Galapagos’ underwater cliffs.
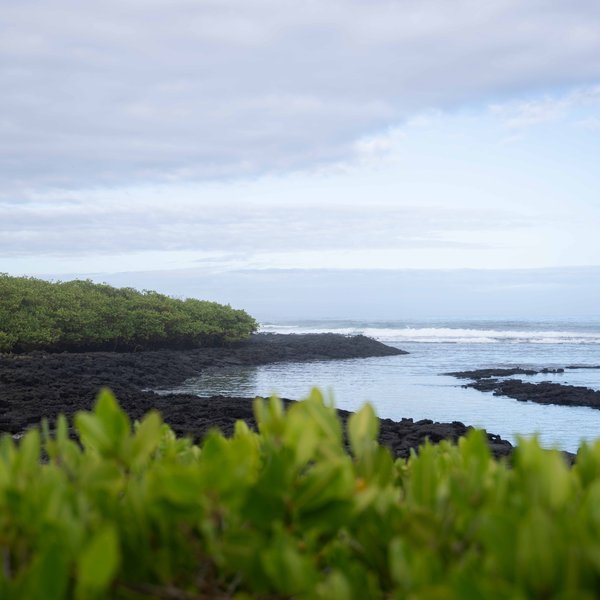

Scientists from the Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF) have, for the first time, assessed the conservation status of mangrove ecosystems in the Galápagos Islands using the Red List of Ecosystems methodology developed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The study concludes that this ecosystem is classified as Vulnerable, underscoring the urgency of its conservation. The full report is available in the EcoEvoRxiv repository.

Scientists from the Charles Darwin Foundation (CDF) have, for the first time, assessed the conservation status of mangrove ecosystems in the Galápagos Islands using the Red List of Ecosystems methodology developed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The study concludes that this ecosystem is classified as Vulnerable, underscoring the urgency of its conservation. The full report is available in the EcoEvoRxiv repository.
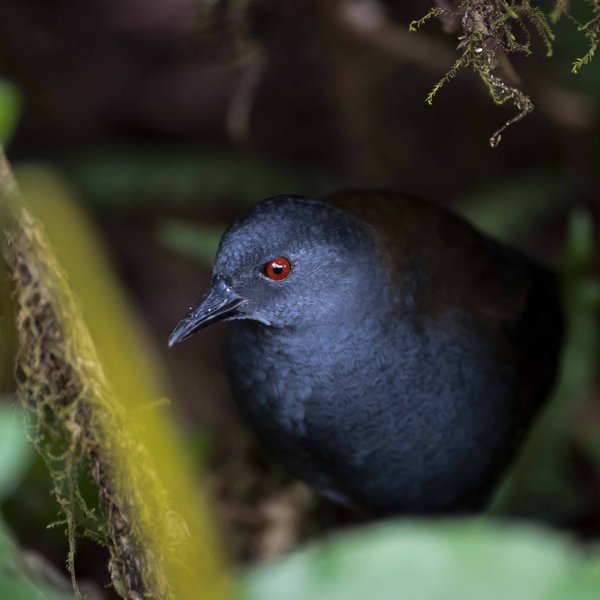

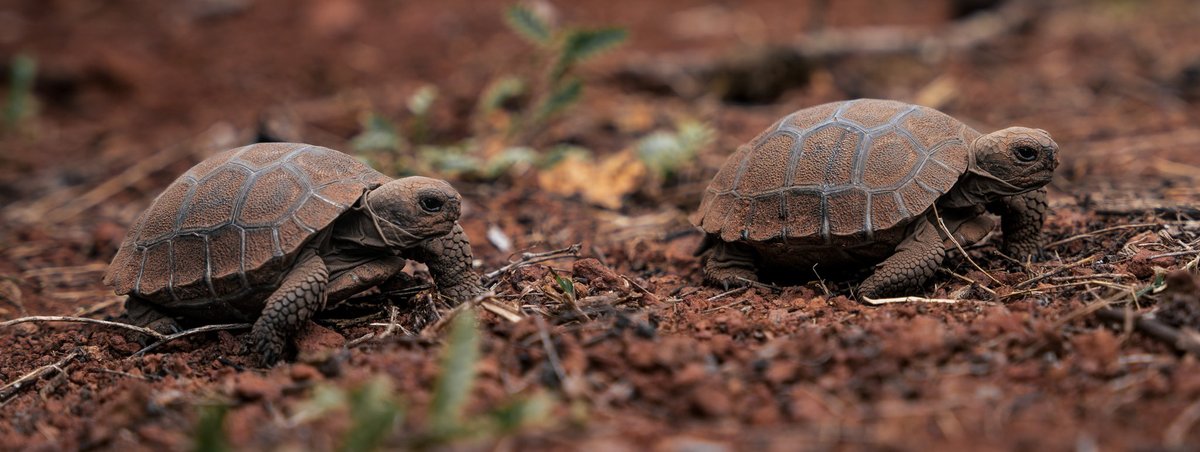
The Galapagos Rail (Laterallus spilonota) has been confirmed on Floreana Island for the first time in 190 years. This follows a 2023 eradication campaign that removed most invasive cats and rats, likely aiding its survival. Researchers will conduct genetic testing to determine if the species recolonized or persisted undetected.
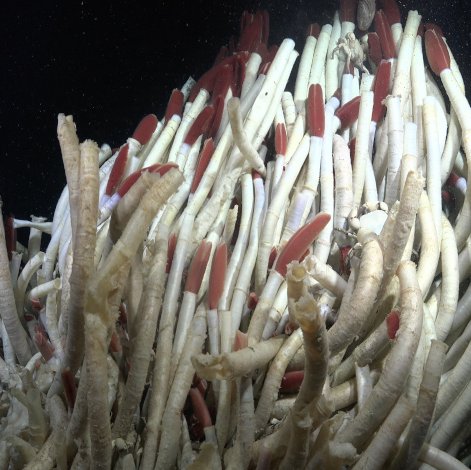
Scientists on a Schmidt Ocean Institute expedition have discovered a new hydrothermal vent field larger than a professional soccer field. The vent field found in the Pacific Ocean off the Western Galápagos Islands consists of five geyser-like chimneys and three hot springs, like those you might see in Yellowstone.












